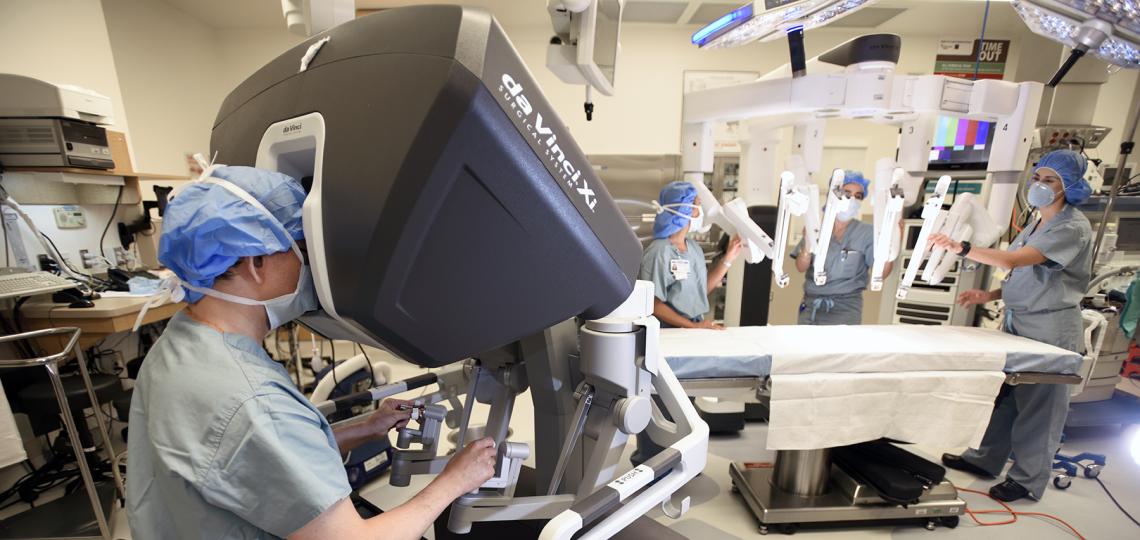
Robotic heart surgery is a minimally invasive approach to cardiac surgery that allows surgeons to perform complex procedures through small incisions, using a robotic system. This technology enhances precision, dexterity, and visualization, offering potential benefits for patients compared to traditional open-heart surgery.
With robotic assistance, surgeons can operate with greater accuracy and control, minimizing trauma to the chest and surrounding tissues. This can lead to less pain, reduced scarring, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times for patients.
Conditions Treated with Robotic Heart Surgery
Robotic surgery can be used to treat a variety of heart conditions, including:
- Aortic Valve Disease: Repairing or replacing the aortic valve.
- Atrial Fibrillation (AFib): Performing the MAZE procedure to correct irregular heart rhythms.
- Atrial Septal Defect (ASD): Closing a hole in the wall between the upper chambers of the heart.
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): Performing coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG).
- Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM): Performing septal myectomy to remove a portion of thickened heart muscle.
- Mitral Valve Disease: Repairing or replacing the mitral valve.
- Pericarditis: Performing pericardiectomy to remove part or all of the pericardium (the sac surrounding the heart).
- Tricuspid Valve Disease: Repairing or replacing the tricuspid valve.
- Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD): Closing a hole in the wall between the lower chambers of the heart.
Benefits of Robotic Heart Surgery
- Smaller incisions: This leads to less pain, reduced scarring, and improved cosmetic results.
- Reduced blood loss: May decrease the need for blood transfusions.
- Lower risk of infection: Smaller incisions reduce the risk of infection.
- Faster recovery: Patients typically experience shorter hospital stays and a quicker return to normal activities.
- Less pain: Reduced post-operative pain.
- Improved cosmetic results: Smaller incisions result in less noticeable scars.
The Robotic Surgical System
The robotic surgical system typically consists of:
- Surgeon console: The surgeon sits at a console and controls the robotic arms.
- Patient cart: The robotic arms are attached to a cart positioned near the patient.
- EndoWrist instruments: Small, wristed instruments that provide a high degree of dexterity and precision.
- 3D high-definition camera: Provides a magnified, three-dimensional view of the surgical field.
Robotic Surgery vs. Traditional Open-Heart Surgery
While robotic surgery offers many benefits, it's not suitable for everyone. Your surgeon will determine the best approach based on your individual needs and the complexity of the procedure.
Traditional Open-Heart Surgery Traditional open-heart surgery involves making a large incision in the chest, through the breastbone (sternum), to access the heart. This approach has been the standard for many decades and is highly effective for a wide range of cardiac procedures. | Robotic Heart Surgery Robotic heart surgery is a minimally invasive approach that uses a robotic system to perform complex procedures through small incisions. The surgeon controls the robotic arms from a console, while a high-definition camera provides a magnified, 3D view of the surgical field. |
Conditions Where Open-Heart Surgery May Be Necessary
| Conditions Where Robotic Surgery May Be Preferred
|
When is Open-Heart Surgery Necessary?
While robotic surgery offers many benefits, it's not suitable for all patients or all types of cardiac procedures. Open-heart surgery may be necessary for:
- Complex cases: Such as those with extensive heart disease or previous cardiac surgeries.
- Emergencies: When there's a need for immediate intervention and robotic surgery is not feasible.
- Patient anatomy: Some patients' anatomy may not be well-suited for a robotic approach.
Choosing the Right Approach
The decision of whether to undergo robotic or traditional open-heart surgery is made on a case-by-case basis. Your surgeon will carefully evaluate your individual needs, medical history, and the complexity of the procedure to determine the most appropriate approach.
Recovery Time
Recovery time for robotic heart surgery is generally shorter than for traditional open-heart surgery. However, the exact recovery time will depend on the specific procedure and your overall health.
Questions to Ask Your Provider
- Am I a candidate for robotic heart surgery?
- What are the risks and benefits of robotic surgery for my condition?
- How long will the surgery take?
- What is the expected recovery time?
- What are the potential complications?




